DevOps is a critical cog within an enterprise’s digital transformation strategy.
After all, it accelerates the rate at which solutions pass through the software development cycle.
Moreover, it safeguards the quality of the solution as it undergoes such development.
As such, DevOps brings several benefits, from speed and quality of innovation to business agility. It does so through a series of philosophies, practices, and tools.
A DevOps platform houses these, unifying the work of application developers and IT teams.
The Definition of DevOps Platforms
According to Gartner, a DevOps platform provides “fully integrated capabilities to enable continuous delivery of software using Agile and DevOps practices.”
These capabilities support the six stages of the software development cycle: planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing and integration, and maintenance.
The analyst also states that DevOps platforms reinforce collaboration, ensure the secure development of software, and monitor various delivery metrics.
Moreover, the platforms help lower friction points within complex toolchains, minimize manual handovers, and increase visibility throughout the development cycle.
DevOps platforms support various use cases, with Gartner sharing the following six examples:
- Agile software delivery
- Mobile app delivery
- Edge computing scenarios
- Regulatory requirements
- Cloud-native application delivery
- Platform engineering
Of course, some platforms will better suit particular use cases.
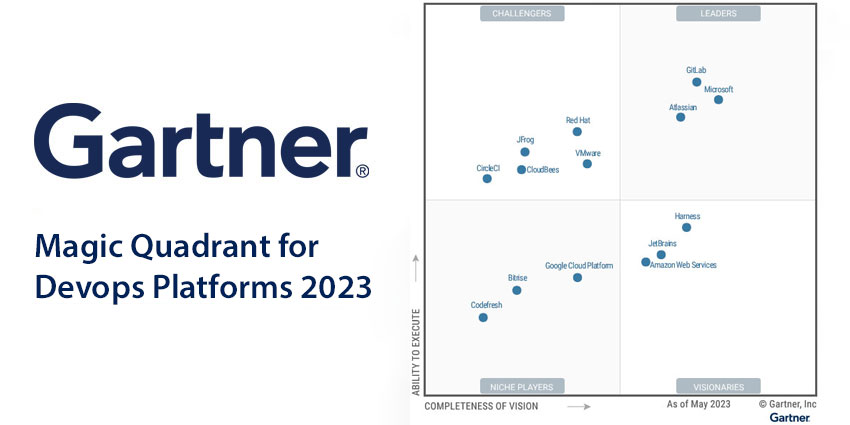
Yet, Gartner has taken a high-level view, splitting 13 vendors into four categories: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players – as the quadrant below showcases.
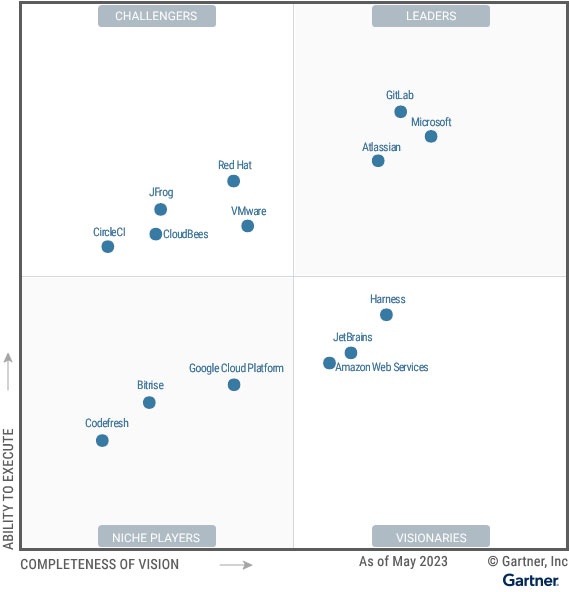
The 2023 DevOps Platforms Magic Quadrant Leaders
Leaders influence the direction of the DevOps space with their thought leadership and services. They back this up with “functionally rich platforms” and a robust capability set throughout the software development lifecycle. As such, these vendors have supported various organizations and use cases. This year’s leaders are:
- GitLab
- Microsoft
- Atlassian
GitLab
GitLab offers complete transparency and traceability across the software delivery pipeline, from base-level code to software apps already in production. That visibility is critical from a security standpoint. Meanwhile, GitLab also builds security into its software development workflows – which Gartner lauds. The market analyst also notes its open-core business model, which allows customers to add capabilities to its core platform, as another significant strength and differentiator.
Microsoft
Microsoft provides two different DevOps platforms: GitHub and Azure DevOps. Yet, customers can procure both with a single license and benefit from several integration points. That may confuse customers. Nonetheless, Microsoft has a thriving developer community that bridges the gap. It also eases the adoption of GitHub workflows and associated solutions. As such, Gartner highlights the community as a core strength alongside Microsoft’s AI-augmented development and cloud development environments.
Atlassian
Atlassian encompasses solutions from Bitbucket, Confluence, Jira Software, Jira Service Management, and Opsgenie. Gartner singles out the combination of Jira Software and Confluence for praise, highlighting how the solutions work well together and enable greater planning and content collaboration. Aside from this, the analyst also sheds a positive light on Atlassian vibrant partner ecosystem – which includes 5,300 apps and integrations – and how the vendor meets the needs of multiple IT and business personas.
The 2023 DevOps Platforms Magic Quadrant Challengers
Challengers can showcase how their solutions have delivered value across particular industries and use cases. That has allowed them to expand their customer base significantly. They have also demonstrated to Gartner their financial strength and commitment to compete at the top of the market. However, they can fall short of leaders in how compelling their roadmap and vision for the future. This year’s challengers are:
- Red Hat
- VMware
- JFrog
- CloudBees
- CircleCI
Red Hat
Combined, the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform and Red Hat OpenShift make for quite a DevOps platform. Yet, the principal plus point of tits solution seems to be in the open-source approach. Indeed, Gartner draws attention to how Red Hat offers Argo CD (OpenShift GitOps) and Tekton (OpenShift Pipelines) as fully supported functions in OpenShift. Meanwhile, the analyst also pays tribute to the platform engineering and hybrid/multi-cloud approach. Yet, Red Hat seemingly limits developer flexibility in bundling Openshift’s capabilities.
VMware
VMware has no problems delivering a flexible platform across multiple levels of the enterprise tech stack. Moreover, it provides both containerized and virtualized software delivery across private, public, and hybrid clouds. That choice is a cornerstone strength – alongside the secure “paved paths to production” it offers and its established client base in VR. Nonetheless, Gartner reveals the quickfire updates across its Tanzu Application Platform have created growing pains, such as limited documentation and revised component names.
JFrog
“Release fast or die” is JFrog’s mantra, and its strength in robust artifact management and distribution is critical here. After all, each developer must sing from the same hymn sheet – and JFrog enables that with the scalable management and distribution of artifacts. Its strengths in supply chain security and storing edge capabilities are also notable strengths, with JFrog paving the way for over-the-air (OTA) updates to IoT and edge devices to enable the latter. Yet, Gartner cautions to limited metrics that offer visibility into software performance.
CloudBees
CloudBees excels in regulated industries, providing the capabilities to comply with many security and compliance standards and curtailing exposure to potential security weaknesses. Gartner notes this – alongside feature management and enterprise-supported Jenkins – as a critical strength. Jenkins is a mainstream open-source automation solution that many DevOps teams utilize to install continuous delivery/continuous deployment (CI/CD) workflows. Unfortunately, CloudBees doesn’t yet have a fully-managed SaaS version of its platform.
CircleCI
Like CloudBees, CircleCI enjoys a significant presence within highly-regulated industries. Much of this is due to its FedRAMP authorization and SOC 2 Type II certification. In addition, the business established a reputation for delivering an easy-to-implement platform and a diverse development environment. As an example of the latter, Circle CI offers numerous resource classes for build runners in legacy, SaaS, and self-hosted modes. Yet, customers have highlighted issues with its GitHub integration and lack of built-in application security securities.
The 2023 DevOps Platforms Magic Quadrant Visionaries
Visionaries understand emerging technologies and business trends that touch the market. They have built these into an innovative product roadmap that aligns well with market demands. However, outside of their current customer base or particular domain, they lack visibility – and sometimes credibility. Moreover, they may lack the resources and expertise to build more market awareness. This year’s visionaries are:
- Harness
- JetBrains
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Harness
Gartner summarizes that Harness is often an ideal fit for organizations that wish to reduce application reliability and security hazards, evaluate software engineering efficiency, and – most critically – implement a cloud-native platform. Indeed, the analyst praises its cloud-native capabilities, such as compliance guardrails, cloud cost optimization, and reliability monitoring. Harness also draws acclaim for its market responsiveness and intelligent workflows. Yet, the provider’s lack of data residency for SaaS beyond North America may concern some.
JetBrains
As per Gartner, businesses that utilize JetBrains’ platform often do so due to its integrated cloud development environment and embedded workstream collaboration. As a prime example of the latter, JetBrains offers collaboration tools such as engagement channels, conversation threads, notifications, polls, and much more. These help to build a team-centric user experience, which Gartner notes as a significant strength. However, the analyst warns that its limited compliance certifications – across various regulators – may perturb potential customers.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS Code Services is often the DevOps platform of choice for organizations striving to develop solutions that integrate natively other AWS services. For instance, a business may connect with AWS Fault Injection Simulator to introduce chaos testing into the software development cycle. That is only one of many possibilities Gartner shares as it lauds these integrations – in addition to AWS’s platform engineering and “cloud-hosted arm builds.” Nonetheless, the analyst cautions to its limited value stream metrics and absence of on-premise options.
The 2023 DevOps Platforms Magic Quadrant Niche Players
Niche players often specialize in a specific subset of DevOps, such as mobile applications. Alternatively, niche players could be small businesses just starting to gain momentum or larger players that do not consider DevOps a strategically significant part of their broad product portfolios. So, while they may trail market leaders on their ability to execute and completeness of vision, making it into the quadrant is impressive in itself. This year’s niche players are:
- Google Cloud Platform
- Bitrise
- Codefresh
Google Cloud Platform
The Google Cloud Platform (GCP) allows users to embed security into software delivery pipelines. That is just one example of its security strengths, alongside its software delivery shield and policy-based deployment controls. The latter ensures only trusted container graphics work in production environments – thus making GCP a well-placed platform for supply chain use cases. However, Gartner points to a few cautions, including restricted value stream metrics and CI/CD capabilities.
Bitrise
Despite its Niche Player status, Bitrise customers score its support services strongly – according to Gartner. The analyst also notes that Bitrise is often a good fit for organizations that wish to develop and scale native and cross-platform mobile apps. Its hosted service for iOS development that offers virtual M1 instances is one critical reason for this. Nevertheless, outside of mobile use cases, Bitrise offers somewhat limited use cases and lacks built-in feature management capabilities.
Codefresh
Codefresh is a platform of choice for many businesses striving to simplify, scale, and secure app development workflows built on Kubernetes. After noting this, Gartner highlights its strengths in GitOps enablement, Argo expertise, and continuous integration. However, the analyst also highlights how the platform is optimized for Kubernetes-Native Applications – making it less agreeable with conventional applications. Other cautions include its scale of operations and few implementation partners.
Catch up on more of the latest CX-related Magic Quadrants by reading the following rundowns:
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Agile Planning Tools 2022
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Digital Experience Platforms 2023
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) 2022