Addressing UI complexity, enabling greater mobility, and augmenting generative AI… these are just some of the emerging trends touching the Sales Force Automation (SFA) Platform market.
Of course, those GenAI moves steal the headlines, with Gartner itself writing many of them.
For instance, the analyst predicts that B2B sellers will execute three-fifths of their work through conversational UIs via GenAI sales technologies by 2028.
Such statistics highlight how SFA Platform buyers should now factor the GenAI roadmap of vendors into their decision-making.
Yet, there are many more elements of the platform to think through. To understand each, here is how Gartner defines the technology.
The Definition of a Sales Force Automation Platform
A Sales Force Automation Platform contains native tools that enable and automate sales activities, processes, and admin responsibilities.
Moreover, it supports the communication of sales teams with customers via different channels and harvests actionable insights via analytics and visualizations from the data it holds.
Such insights enhance contact, pipeline, and opportunity management while paving the way for guided selling and improved forecasts.
Yet, a modern SFA Platform goes beyond internal use cases. Customers and prospects may access parts of the platform, engage in shared experiences, and collaborate with sales personnel.
Additional capabilities now considered standard include: Mobile, IoT devices, and bot features, alongside partner relationship management functionalities, a proposal and quote builder, as well as a composable architecture.
Then, there are the other features that some vendors choose to add to their platforms. According to Gartner, these include:
- Configure Price Quote (CPQ) apps or suites
- Digital sales rooms
- Revenue intelligence
- Sales engagement
- Revenue enablement (digital content management, training and coaching)
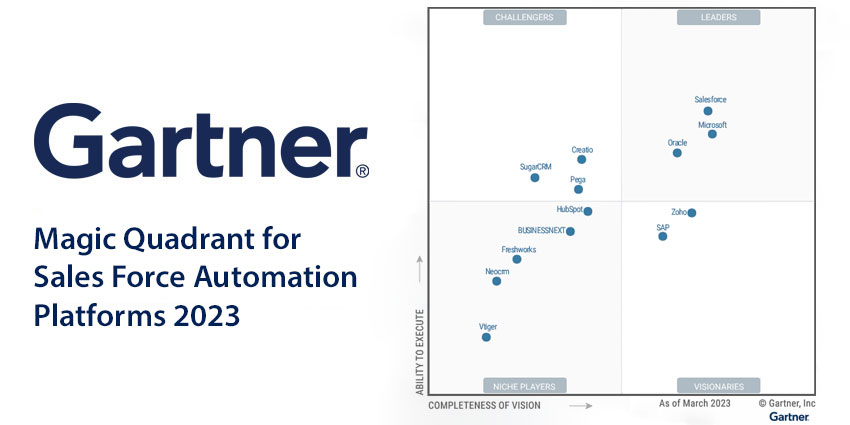
After establishing such fundamentals, the analyst split the 13 participating vendors in the report into four categories: Leaders, Challenges, Visionaries, and Niche Players. Here, we review them all.
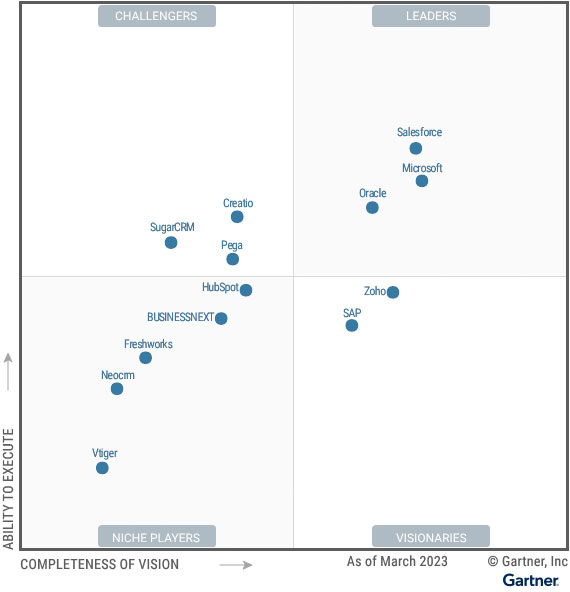
Gartner Magic Quadrant Leaders
Leaders in the Magic Quadrant pair a clear, cutting-edge vision with an ability to demonstrate “solid” business results. They can also showcase a global presence across several sectors, alongside an ability to continually secure above-average customer experience scores. This year’s leaders are:
- Salesforce
- Microsoft
- Oracle
Salesforce
Within Sales Cloud, Salesforce offers “strong” Partner Relationship Management capabilities. These enable complete partner-driven sales cycles, which the CRM leader augments with its Revenue Cloud solution to provide self-service CPQ. That is an advanced capability Gartner notes as a critical strength – alongside the vendor’s product portfolio, ecosystem, and customer community. Meanwhile, Gartner does note pricing increases and packaging as a caution. Yet, it’s worth adding that those price hikes are the first Salesforce has implemented in seven years.
Microsoft
Microsoft has drawn closer to Salesforce in this year’s edition of the Magic Quadrant. A likely cause is its push into generative AI and “compelling roadmap”. Gartner acknowledges this while noting Microsoft’s AI innovation as a fundamental strength, cherry-picking its developments in real-time insight capture, SMS, and “sales sequence effectiveness measurements”. Alongside this, the analyst notes its sales productivity and customer-centric product strategy as significant plus points. Like with Salesforce, Microsoft does – however – fall back on its cost complexity.
Oracle
The innovation across Oracle Sales has gathered great momentum in the past 12 months, with Gartner shedding a positive light on the new embedded dynamic sales guidance solution and configurable similar-account-analysis model. Such innovation, Oracle’s market responsiveness, and its robust capabilities across mobile, devices, and bots have helped to cement the vendor’s leading market position. Nonetheless, the analyst suggests the vendor could do more to support end-users in seeping further value from the platform.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Challengers
Challengers in the Magic Quadrant reel in a high volume of new business, competing with SFA leaders across the globe. Moreover, they have developed a sophisticated systems architecture and understand the evolving needs of sales teams. Where they fall behind leaders is in leading customers into new functional remits with a robust vision. This year’s leaders are:
- Creatio
- Pegasystems
- SugarCRM
Creatio
Like Oracle, Creatio gains plaudits for its guided selling capabilities. An excellent example is how the Sales Creatio platform presents statistical correlations on-screen – showing the potential impact of various actions the salesperson may take. That ability to optimize decision-making garners positive recognition from Gartner – as does Creatio’s buoyant customer community and vertical strategy that covers 20 industries. Where the vendor starts to slip back is in its post-sale customer success management, with Creatio no longer providing in-house consulting services.
Pegasystems
The Pega Sales Automation platform flexes across sectors, with AI and machine learning tailored to specific industries – including healthcare, finance, and telecommunications, amongst others. Gartner considers this strategy a significant strength, alongside Pega’s lead management functionality, varied deployment options, and overall product strategy. The latter covers a “rich portfolio” of critical SFA capabilities – as per the analyst. Despite this, Gartner cautions that Pega trails many of its rivals in the pace at which it releases product enhancements, citing customer feedback.
SugarCRM
Gartner gives plaudits to the support infrastructure SugarCRM places around Sugar Sell. An excellent example is in the vendor’s implementation services, which include specialist support for data migration, integrations, and sales management. Also, the report notes SugarCRM’s customer success and sales strategies as plus points, with the provider adding approximately 50 new channel partners in the past year to aid the latter. Unfortunately, its product strategy does seemingly lag behind rivals. For instance, Sugar Sell still does not include ML-based, next-best-action recommendations.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Visionaries
Visionaries in the Magic Quadrant are at the forefront of product and delivery model innovation. In addition, they frequently anticipate emerging market trends, explore new possibilities, and move the market into new spaces. However, they often trail leaders in execution. This year’s visionaries are:
- Zoho
- SAP
Zoho
With 50+ native products and a lower price point, Zoho often fits the bill for brands wishing to jumpstart their deployments with a smaller vendor stack that comes at a reduced cost. Gartner highlights this strategy as a core strength, alongside the vendor’s customer community and market responsiveness. Its new CPQ engine, churn prediction, and sentiment analysis features exemplify this. Yet, despite its deep native portfolio, the vendor offers a shallow marketplace with little more than 100 sales-specific APIs available to businesses wishing to diversify their SFA Platform.
SAP
SAP demonstrates a deep understanding of the SFA market. Its Microsoft Teams integration, omnichannel sales engagement tools, and real-time coaching capabilities underline that. Moreover, Gartner highlights SAP’s expertise across complex use cases and its no-extra-cost AI and machine learning features as significant strengths. An excellent example of the latter is the free AI-infused scoring mechanisms across SAP Sales Cloud. Nevertheless, Gartner has cautioned that the vendor has made “no notable releases” of the platform in the past year.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Niche Players
Niche Players in the Magic Quadrant can deliver a considerable ROI, especially in particular corners of the market. Yet, they often lack functional components, which limits their overall appeal. They can also lag in their business execution, enterprise suitability, and implementation track record. This year’s niche players are:
- HubSpot
- BUSINESSNEXT
- Freshworks
- Neocrm
- Vtiger
HubSpot
HubSpot differentiates Sales Hub with its out-of-the-box integrations, with a library of 1,400 APIs that features more than 550 applications in the sales category. Gartner notes this but also lauds the scope of native capabilities within the SFA platform. Indeed, the analyst notes that Sales Hub includes many native features ordinarily considered add-ons. Some examples include one-to-one messaging, suggested send times, and “automated sequences for sales development reps”. Nonetheless, HubSpot trails in its large enterprise services and contract flexibility.
BUSINESSNEXT
Formerly known as CRMNEXT, BUSINESSNEXT demonstrates considerable platform flexibility, as users can harness its modular architecture to rearrange various tech components. Alongside this, customers can choose from 12 preassembled products with multiple deployment options. Gartner finds many advantages to this strategy and commends the vendor’s AI-fueled account and contact scoring mechanism that learns from successful sales cycles. However, the analyst finds fault in BUSINESSNEXT’s few implementation partners and the absence of an ISV-driven marketplace.
Freshworks
Freshworks has established a reputation for low Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), with customers praising its “affordable pricing” and free-to-use edition. The analyst highlights this as a strength, alongside the vendor’s customer success resources and collaboration features. It singles out Freshsales’ unified messaging solution as an excellent example of the latter, allowing teams to communicate with buyers across WhatsApp, Apple Messages, and various UC platforms. Despite all this, Freshworks lacks several product features in critical areas, including conversational intelligence.
Neocrm
With a deep customer base in China, Neocrm meets the local preference for mobile interactions with advanced capabilities in this arena. For instance, it records interactions across channels such as WeCom/WeChat and Tencent and extracts insight with native conversational intelligence tools. Gartner pinpoints such mobile support as a strength, alongside the compelling visualizations of the insights those intelligence and analytics tools unearth. However, the lack of AI and machine learning across the platform is palpable, with manual rules and triggers ruling the roost.
Vtiger
With an “always-free” edition of its Vtiger One platform available via self-signup, Vtiger often appeals to the SMB market. Indeed, Gartner notes that it is a “solid offering” for smaller businesses beginning their journeys into the fun-filled world of CRM. Its helpful features for that SMB segment – particularly those that cover activity and opportunity management– and buyer engagement tools also win plaudits from Gartner. Moreover, Vtiger offers advanced AI capabilities, yet these come at a cost that stacks up. That concerns Gartner, alongside its unripe forecast management functionalities.
What Has Changed Since 2022?
Despite GenAI and other new-fangled trends converging on the Sales Force Automation space, the positions of most vendors are relatively similar to the 2022 edition of the same Magic Quadrant.
One of the more significant shifts is in Microsoft’s positioning. Indeed, it has pushed further right, which underlines its maturing SFA vision – with GenAI likely playing a substantial role.
Nonetheless, Salesforce stays closest to the top-right corner of the matrix, ahead of Microsoft and fellow market leader Oracle.
Other positive moves include Pega, Zoho, and HubSpot pushing closer to that leader quadrant.
Unfortunately, BUSINESSNEXT has lost its visionary status, joining the niche player square. Meanwhile, SugarCRM and Freshworks also appear to have slipped backward.
Finally, Zendesk has dropped off the quadrant completely, with Gartner revealing that it no longer meets the inclusion criteria.
Uncover some of our other rundowns of the Gartner Magic Quadrant reports below:
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) 2023
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Analytics and Business Intelligence Platforms 2023
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Conversational AI Platforms 2023