Google’s adventures in the artificial intelligence landscape are growing increasingly advanced of late. Not only have we seen the arrival of the Google Contact Center AI, but there’s also a new conversational chatbot on the horizon.
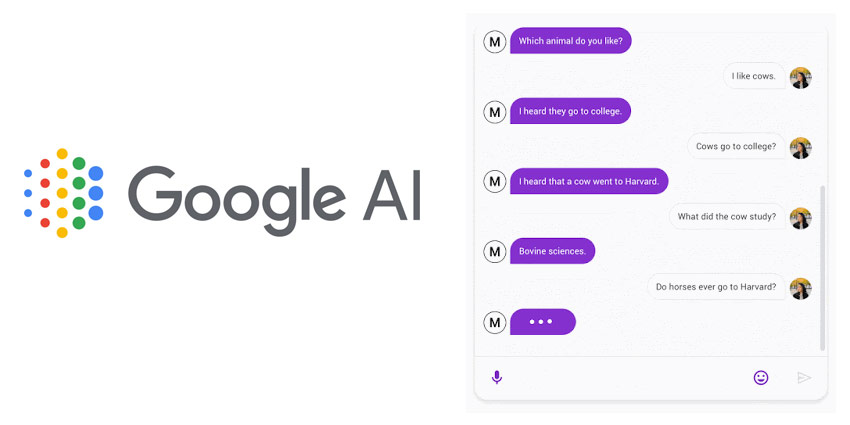
In the “Towards a Human-like open-domain chatbot” presentation, Google introduced the world to its Meena solution. The neural conversational model comes with training from 2.6 billion parameters, offering an in-depth conversational experience that feels more natural and human than ever. Google notes that Meena is capable of conducting conversations that feel more organic and specific than many of the existing chatbots on the landscape today.
The improvements made to the Meena model come from a new human evaluation metric strategy that Google believes should be used by all open-domain chatbots.
The Sensibleness and Specificity Average
The metric that has made Meena so impressive is the Sensibleness and Specificity Average (SSA). This basically captures crucial attributes for natural human conversation. According to Google, perplexity – one of the common metrics that is available in most neural conversational models, already collates with this new concept of SSA.
Using the idea of SSA, Google has been able to transform Meena into an end-to-end neural conversation system that can respond sensibly and almost thoughtfully to the context of a conversation. According to Google, the training objective is to reduce perplexity and uncertainty in predicting conversational outcomes. Underneath Meena is the Transform Seq2seq foundation – an architecture that was created using neural architecture study to improve responses to perplexity.
Meena comes with a single encoder transformer block, and 13 evolved decoder blocks. The encoder helps her to process the context of the conversation and understand what customers have already said in a conversation. On the other hand, the decoder blocks use the information to formulate useful and natural responses.
Taking Chatbots to the Next Level
Meena was trained using a number of ‘tree threads’, where every reply in a thread is viewed as a singular conversational turn. The Meena model’s 2.6 billion parameters means that it has a massive network of potential responses and contextual information to draw from when responding to queries and conversations.
Going forward, Google plans to continue using what it has learned from the Meena model update about things like SSA and decoder models to make chatbots more incredible. Google even noted that it may be looking into things like factuality and personality more aggressively in future works, to make interactions with similar chatbots more memorable, accurate and engaging. At the same time, Google has noted that tackling bias and safety in models like Meena is crucial for the company, and that it will be evaluating the risks in this in the future.