CRM platforms are swallowing up the customer service stack.
Now, they include more customer engagement channels, automate more service workflows, and leverage more advanced AI.
Such AI includes conversational intelligence tools, filling up the platform with new insights – including customer sentiment, intent, and even automated call notes.
All these trends – and several others – have gained traction since Gartner’s previous Magic Quadrant for CRM Customer Engagement Center, published in 2021.
Yet, despite all this disruption, the same CRM providers crop up in the analyst’s latest market evaluation, which pinpoints four leaders.
→ THE 2024 Edition: Check out CX Today’s coverage of the latest Magic Quadrant for CRM Customer Engagement Center.
The Definition of CRM Customer Engagement Center
According to Gartner, a CRM customer engagement center is a “cohesive” software suite that revolves around case management.
Indeed, the suite orchestrates, data, systems, workflows, and various other resources to support businesses in delivering their desired service experience across cases.
That service experience enriches customer engagements via personalization, knowledge management, and – oftentimes – self-service capabilities.
Yet, there are many more features within a CRM Customer Engagement Center, as evident in Gartner’s list of functional requirements and design considerations:
- Scalable cloud-based systems
- Digital engagement channels
- Unification of digital and voice touchpoints
- Use of contextual knowledge management
- Automation of engagements
- Proactive messaging to customers
- Workforce engagement management (WEM) components
- An ecosystem for functional enrichment
- Low-code development
Yet, other features extend the core CRM Customer Engagement Center offering. These include VoC tools, IoT and RPA connections, and customer success functionality – amongst several others.
Each highlights how the CRM is now much more than a system of record for customer conversations and how much Gartner had to consider in its market investigation.
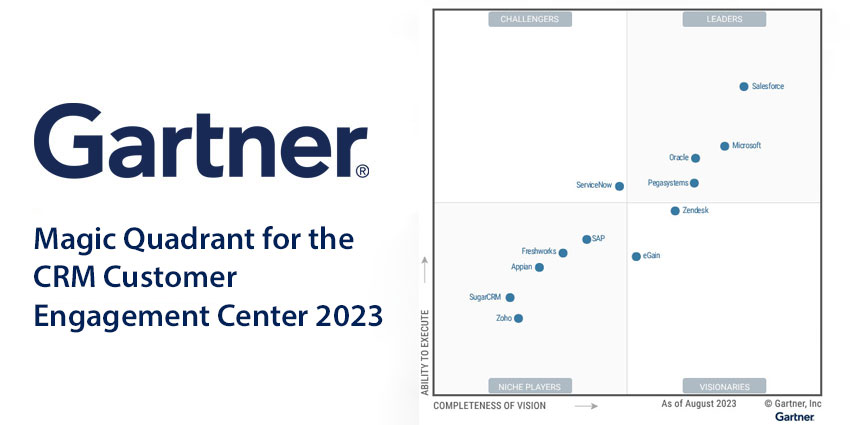
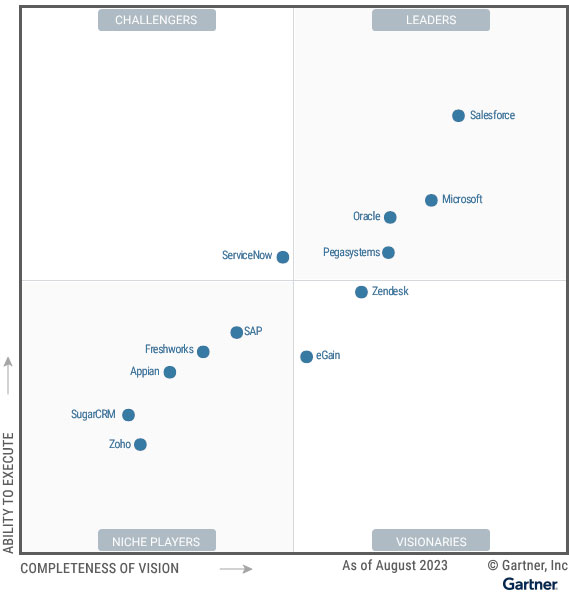
Nevertheless, the analyst managed to stay on top of all this, splitting 12 prominent providers into four groups: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Leaders
Leaders in the Gartner Magic Quadrant help to define the market’s direction through products, services, and customer experience. They also offer a comprehensive platform that flexes to meet requirements across geographies and sectors. Finally, they pair their solution and innovation leadership with a clear vision of capitalizing on emerging technologies. This year’s leaders are:
- Salesforce
- Microsoft
- Oracle
- Pegasystems
Salesforce
Gartner commends Salesforce Service Cloud for its “overall viability and innovation”, which appeals to diverse sectors and market segments. In doing so, the analyst notes that the CRM is now Salesforce’s largest revenue-generating product – providing a sense of the solution’s long-term viability. Moreover, Gartner praises the vendor’s product strategy, which utilizes customer feedback to closely consider how organizations can more easily understand and leverage new features.
Microsoft
Microsoft is innovating at a rate of knots, rapidly releasing new agent productivity, collaboration, and GenAI features across the platform. The vendor has also substantially enhanced the messaging and voice services within Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service. Gartner notes this fast innovation as a significant strength, alongside Microsoft’s mounting market presence and expanding platform. The addition of Nuance, the conversational AI and healthcare tech provider, exemplifies the latter.
Oracle
A core strength of Oracle’s Fusion Service offering is its unified agent workspace. Gartner recognizes this, lauding the streamlined agent UI, its activity stream panels, and other nifty features. “Smart text hashtags” – which help to automate customer responses via knowledge from a prewritten library – is an excellent example. In addition, the analyst notes Oracle’s collaboration capabilities and unified enterprise platform – which includes ERP, SCM, and HCM solutions – as prominent plus points.
Pegasystems
Pega Customer Service has an automation core, which enables AI-powered decisioning, automatic cross-workflow referencing, and AI-driven end-to-end customer service workflows. As such, it’s no surprise that Garter highlights Pegasystems’ process automation and augmentation as a critical strength, alongside its extensive integration ecosystem and engagement channels. The latter includes “long-running” asynchronous messaging, digital- and dialed-voice, and third-party messaging apps.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Challengers
Challengers in the Gartner Magic Quadrant enjoy a significant market presence, benefiting from specific sector expertise and robust, expanding relationships with the wider install base. In forging these relationships, these vendors understand their client’s evolving needs, yet may not be best-positioned to make the most of broader, emerging market trends. This year’s sole challenger is:
- ServiceNow
ServiceNow
ServiceNow leads the ITSM market and has done an excellent job cross-selling its Customer Service Management platform. Noting this, Gartner highlights the solution’s overall visibility as a strength emboldened by its tight integrations with “hundreds” of familiar enterprise systems. The analyst also suggests its industry-specific workflows and platform capabilities – especially in regards to RPA and back-end services – are differentiators. Yet, some find its pricing and licensing structure complex.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Visionaries
Visionaries in the Gartner Magic Quadrant lead many market rivals in developing innovative solutions and delivery models. Moreover, they often anticipate market shifts and influence the direction of the CRM space. Yet, visionaries typically trail in execution and track record. Meanwhile, they may need to strengthen partnerships and integrations to challenge leaders. This year’s visionaries are:
- Zendesk
- eGain
Zendesk
Zendesk has earned a reputation for delivering easy-to-use software. That is evident in its platform’s UI, admin controls, and dashboards, with the latter offering high visibility into conversation assignments, workloads, and customer service KPIs. In line with this, Gartner praises its AI innovation and brand awareness, with Zendesk often making it onto client shortlists for CRM Customer Engagement Centers. Yet, it seems to lag in its customizability across advanced enterprise processes.
eGain
Gartner notes AI and automation are crucial strengths for eGain. In doing so, the analyst points to its new Instant Answers solution, which allows companies to configure their own virtual assistant for agent-assist use cases. Composability and product functionality are further plusses, with the vendor taking on a knowledge-centric approach to the latter. That suits businesses with strict content access management processes. However, Gartner cautions of its limited marketplace and app development.
Gartner Magic Quadrant Niche Players
Niche Players in the Gartner Magic Quadrant have achieved a significant market share. Also, they often meet customer expectations across particular industries and regions. Yet, their focus is sometimes smaller, and they may struggle to keep pace with broader demands in the market. Nonetheless, the price-to-value ratio of their platform allows some to compete at the market’s forefront. This year’s niche players are:
- SAP
- Freshworks
- Appian
- SugarCRM
- Zoho
SAP
SAP Service Cloud is a stalwart CRM platform that closely connects with the vendor’s ERP to provide a “360-degree view” of the customer. Agents may also enjoy a unified workspace, which Gartner describes as “well-organized”, and assistive features such as rapid interaction summarization. The analyst also notes SAP’s track record for meeting customer requirements. Yet, it suggests that businesses may find deployments complex and that innovations target broader SAP customers.
Freshworks
Freshworks benefits from a slick sales process, with free trials and a “freemium” licensing model that businesses can test without risk of lock-in. The vendor complements this with a bustling marketplace and high ease of implementation. Indeed, Gartner confirms that most customers can deploy the solution without support from the vendor or third-party services. Unfortunately, some clients report dissatisfaction with its product support responsiveness and limited customization.
Appian
Appian is often the CRM businesses turn to when they want a highly customizable solution to orchestrate unique service processes. There are also advanced automation capabilities within its suite to power these processes and take them beyond customer support. Its extensive integration support is also beneficial here. Gartner highlights all these strengths but warns of high implementation complexity and limited support beyond finance, insurance, and government.
SugarCRM
According to Gartner, Sugar Serve is often a good fit for “budget-conscious environments”, delivering bang for a business’s buck. However, it still has differentiative features, including a Sugar Connect Outlook and Gmail integration that allows users to email customers from a familiar environment. Moreover, Gartner highlights ease of implementation and cross-functional process synergies as core strengths. Yet, the analyst warns of limited innovation, visibility, and marketplace partners.
Zoho
Zoho’s Customer Engagement CRM product is available as a bundle or two solutions: Zoho One and Zoho CRM Plus. Gartner notes the “pricing and value” of the former as a significant strength. Others include its ease of implementation and field service capabilities, which meet remote device-support requirements. As a result, businesses can orchestrate service processes for field service personnel on a single platform. However, in the broader sense, there’s little differentiation in Zoho’s offering.
What Has Changed Since the Previous Magic Quadrant?
In short, everything. That includes Gartner’s market definition, critical capabilities, and scoring criteria – which are markedly different from the previous 2021 edition.
As such, Gartner has asked to avoid all direct comparisons.
What is worth noting – however – are the changes in participating providers.
While there are no new names, Creatio and CRMNEXT no longer feature as they don’t meet the updated inclusion criteria.
In the case of Creatio, it couldn’t demonstrate a significant market presence in three regions. Meanwhile, CRMNEXT missed out after failing to meet the criteria for “financial achievement.”
Finally, Ivanti (Cherwell) and Verint no longer pursue the CRM customer engagement center market – targeting adjacent spaces.
Deep dive into some of our other Magic Quadrant report rundowns below:
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Multichannel Marketing Hubs 2023
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for B2B Marketing Automation Platforms 2023
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) 2023